|
Property
|
Description
|
|
Class
|
|
|
Superclass
|
|
|
Subclass
|
|
|
Definition
|
An instance of this DRM class specifies a unit vector, the
meaning of which is specified by its
vector_type field.
The unit_vector
field specifies the unit vector.
The vector_type field
specifies the semantic meaning of the vector data
being represented by the given instance of
<DRM Reference Vector>.
|
|
Clarifications
|
None.
|
|
Class diagram
|
Figure 6.257 —
DRM_Reference_Vector
|
|
Inherited field elements
|
|
Field name
|
Range
|
Field data type
|
None |
|
|
|
|
Field elements
|
|
Associated to (one-way) (inherited) |
|
Associated to (one-way) |
|
Associated by (one-way) (inherited) |
|
Associated by (one-way) |
|
Associated with (two-way) (inherited) |
|
Associated with (two-way) |
|
Composed of (two-way) (inherited) |
|
Composed of (two-way) |
|
Composed of (two-way metadata) (inherited) |
|
Composed of (two-way metadata) |
|
Component of (two-way) (inherited) |
|
Component of (two-way) |
|
|
Constraints
|
|
|
Example(s)
|
Consider a <DRM Polygon> instance specified in
a LSR 3D SRF,
for which a data provider wishes to explicitly provide the
surface normal vector so that consumers do not need to calculate
the surface normal when consuming that particular
<DRM Polygon> instance.
The data provider specifies this vector information as a
<DRM Reference Vector> component
of the <DRM Polygon> instance as shown in
Figure 6.258:
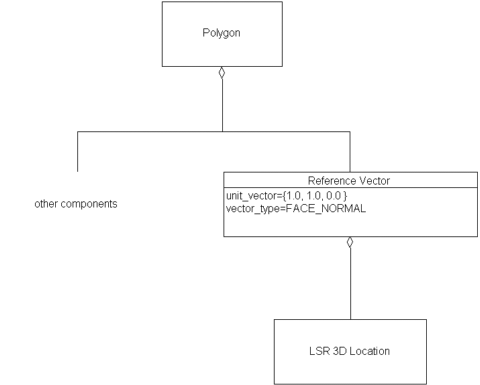
Figure 6.258 — <DRM Reference Vector> example
1
Since the <DRM Reference Vector>
instance
is a component of a <DRM Polygon> instance, it
specifies a <DRM LSR 3D Location>
component in order to comply with
the constraint specified in
6.2.50 Required reference vector location.
Consider a <DRM Reference Vector>
instance contained by a
<DRM Polygon> instance, representing a normal vector that is used
for rendering purposes (that is, to calculate colour and shading when rendering
the <DRM Polygon>). This
<DRM Reference Vector> would have a
vector_type of
RENDERING_NORMAL.
Consider a <DRM Polygon> instance F that
represents an ECC_FENCE, where F is a quadrilateral
as shown in Figure 6.259.
Figure 6.259 — Example quadrilateral
F is instanced on some terrain representation, such that the
plane of F is perpendicular to the surrounding terrain.
F has radar cross sections that are dependent on aspect angles
(azimuth and elevation). These aspect angles are defined with
respect to F’s normal vector and F’s azimuth vector.
Consequently, F has two components as shown in
Figure 6.260:
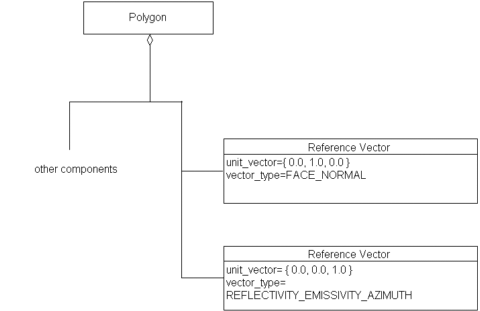
Figure 6.260 — Two <DRM Reference Vector>
components
The FACE_NORMAL
<DRM Reference Vector> instance is the unit vector
that is perpendicular to the plane of F, and that points away from F
on its outside face. The
Reference_Vector_Type
<DRM Reference Vector>
instance
is the unit vector that lies in the plane of F and points straight
up.
A segment of the road has a retro-reflector
on it and is modeled as a <DRM Line> instance. The
<DRM Line> instance has a normal vector that is
perpendicular to it and an azimuth reference parallel to it. This is
sufficient to describe radar cross sections of the road as a function of
aspect angles. However, the normal vector for the infrared bands depends
on the orientation of the retro-reflector, not the road. This is because
radars see the road but infrared see the retro-
reflector. In this example, the <DRM Line> instance has
four <DRM Reference Vector> components
(radar-normal, radar-azimuth, infrared-normal, and infrared-azimuth).
A normal vector used for reflectivity/emissivity calculations. This would
have a vector_type of
REFLECTIVITY_EMISSIVITY_NORMAL.
A vector specifying the direction an
<DRM Infinite Light> illuminates. This would
have a vector_type of
LIGHT_DIRECTION.
|